Freeze drying breast milk is a common method used to preserve the nutritional properties, but many parents wonder if the freeze drying process leads to a loss of nutrients. Research has been conducted to assess the impact of freeze drying on breast milk, and the findings suggest that freeze dried human breast milk retains nearly all nutrients essential for infants.
This article will explore the effectiveness of freeze drying breast milk and provide scientific evidence to support the claim that freeze dried breast milk retains its nutritional value.
Key Takeaways
- Freeze drying breast milk preserves its nutritional properties and retains essential nutrients.
- Extensive research has shown that freeze dried breast milk retains nearly all nutrients essential for infants.
- Freeze drying technology uses sublimation to remove water from breast milk, leaving behind a stable powder.
- Freeze dried breast milk offers various practical benefits, including enhanced shelf-life and convenience for busy parents.
- Freeze dried breast milk can be fortified into babies’ foods and customized with your nutritionist for specific nutritional needs.
Understanding Freeze Drying Technology for Breast Milk
In this section, we will delve into the freeze drying process and its application to mature human milk preservation. Freeze drying, also known as lyophilization, is a state-of-the-art technology that effectively preserves the nutritional properties of breast milk. By removing water from the breast milk through sublimation, freeze drying creates a stable powder that can be reconstituted later while retaining its original nutritional content.
The Scientific Principle Behind Lyophilization
Lyophilization works on the principle of sublimation, which involves transforming water from a solid (ice) directly into vapor (water vapor) without passing through the liquid phase. This process occurs under low pressure and at extremely low temperatures, typically below freezing. By subjecting the breast milk to these specific conditions, freeze drying technology effectively removes water from fresh breast milk without compromising its nutritional value.
Comparing Freeze Drying with Traditional Freezing
When comparing freeze drying with traditional freezing methods, such as conventional freezer storage, the advantages of freeze drying become evident. While traditional freezing methods may gradually alter the taste, texture, and nutritional content of breast milk, freeze drying minimizes these changes. Traditional freezing can lead to the separation of fats and water, affecting the composition and quality of breast milk. In contrast, freeze drying retains the original composition of breast milk and prevents nutrient loss.
Freeze Dried Breast Milk Retains Nearly All Nutrients
Breast milk is rich in essential macronutrients and micronutrients that play a vital role in supporting infant growth and development. Many parents are concerned about the impact of freeze drying on the nutritional content of breast milk. However, research has shown that freeze drying effectively preserves the fundamental nutrients in breast milk, ensuring that infants receive the necessary sustenance for their well-being.
Energy Content and Nutrients
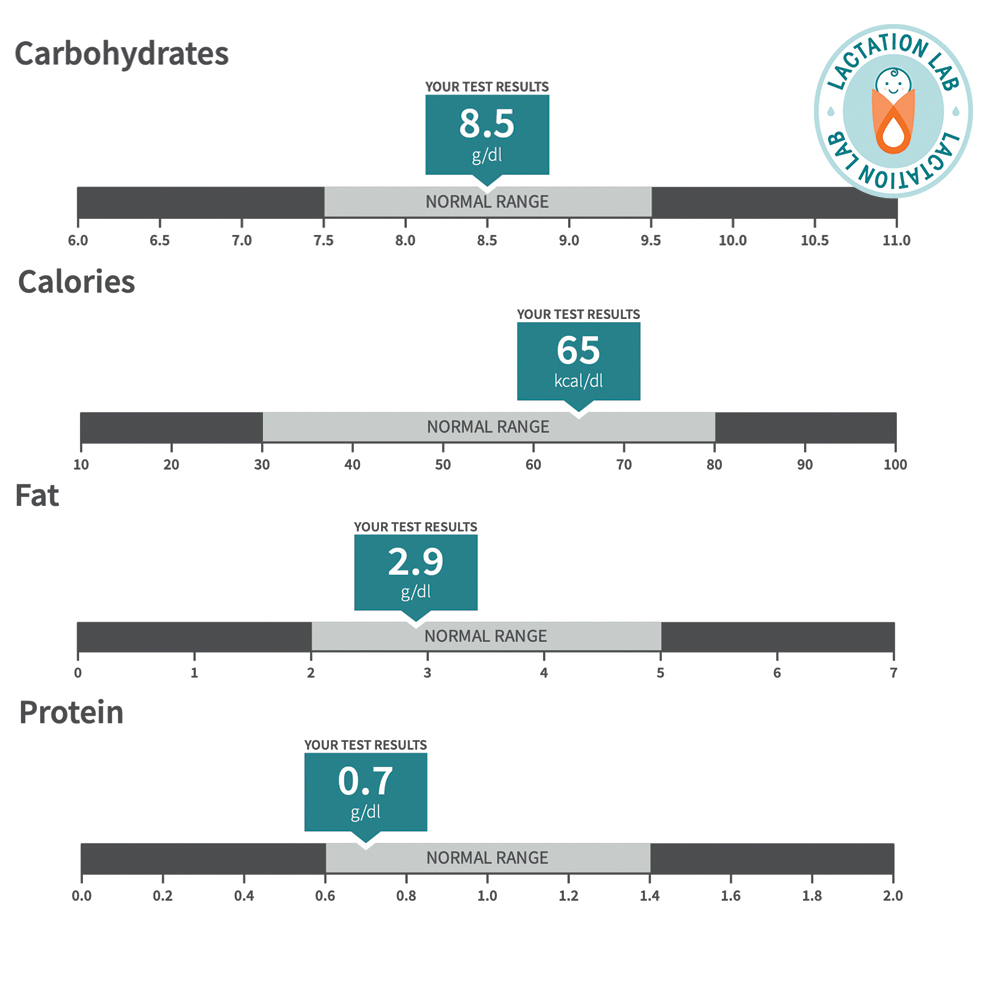
First, it’s important to understand human milk composition including the main nutrients. Human breast milk is uniquely tailored to meet the nutritional needs of infants. It contains about 87–88% water and provides 65–70 kcal per 100 mL. The remaining solids consist of essential macronutrients, carbohydrates, protein, and fat, along with vital micronutrients, antibodies, growth factors, and bioactive compounds.
Macronutrients in HBM include:
- Carbohydrates: Primarily lactose and human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), which support gut health, mineral absorption, and immunity.
- Proteins: A blend of whey and casein, rich in bioactive compounds like lactoferrin and immunoglobulin A, essential for immune defense and digestion.
- Fats: Provide around 50% of total energy, containing essential fatty acids like DHA and arachidonic acid, crucial for brain and eye development.
Micronutrient levels are generally sufficient, though vitamins D and K may require supplementation in breastfed infants. Minerals like iron, despite low concentrations, are highly bioavailable.
Breast Milk Composition Chart
Component | Colostrum (1–5 days) | Mature Milk (>14 days) | Notes |
Energy | 50–60 kcal/100 mL | 65–70 kcal/100 mL | Energy increases as milk matures |
Carbohydrates | 50–62 g/L | 60–70 g/L | Mainly lactose; HMOs support gut and immune health |
Protein | 14–16 g/L | 8–10 g/L | Higher in colostrum for early immunity |
Fat | 15–20 g/L | 35–40 g/L | Fat content increases over time |
Vitamin D | Low | Low | Supplementation often recommended |
Vitamin K | Low | Low | Requires supplementation after birth |
Iron | 0.5–1.0 mg/L | 0.3–0.7 mg/L | Highly bioavailable despite low levels |
Breast milk’s composition changes over time and varies with maternal health, diet, and feeding stage. This natural variability ensures personalized nutrition for each infant.
Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Fats Retained
One of the key concerns regarding freeze drying breast milk is the retention of these essential macronutrients. Studies have demonstrated that freeze drying does not lead to significant loss of these crucial nutrients. When you store breast milk via freeze drying, the process effectively removes water from the milk while preserving the macronutrient structure, ensuring that infants continue to receive the necessary proteins, carbohydrates, and fats required for healthy growth.
Immune Factors: Antibodies IgA, IgG, and IgM Retention
Breast milk is known to contain immune factors, including antibodies IgA, IgG, and IgM, which provide vital protection against infections and diseases. Fortunately, freeze drying does not compromise the retention of these immune factors. Research studies have confirmed that antibodies present in breast milk remain intact even after the freeze drying process.
This means that freeze dried breast milk continues to provide immune support to infants, bolstering their immune systems and helping them combat infections. With freeze drying, you build you own milk bank with all the necessary immune building ingredients.
Sustaining Probiotic Bacteria and Prebiotic Functions
In addition to immune factors, breast milk is a natural source of probiotic bacteria that promote a healthy gut microbiome in infants. Probiotics support digestion, boost the immune system, and contribute to overall gut health.
Freeze drying maintains the viability of these beneficial probiotic bacteria, ensuring that infants receive the full potential of the gut health benefits offered by breast milk. By preserving probiotics, freeze dried breast milk helps establish a healthy microbial balance in the gastrointestinal tract, protecting against gastrointestinal problems and supporting immune function.
Furthermore, breast milk contains prebiotic functions. These prebiotics serve as food for the probiotic bacteria in the infant’s gut, stimulating their growth and promoting a healthy digestive system.
Freeze drying maintains the prebiotic functions of breast milk, providing essential nourishment for the probiotic bacteria to thrive in the infant’s gut. This symbiotic relationship between probiotics and prebiotics contributes to a strong immune system and optimal gastrointestinal health in infants.
Freeze Drying’s Impact on Micronutrients and Vitamins
In addition to macronutrients and immune factors, fresh milk also contains important micronutrients and vitamins that contribute to infant health and development. The freeze drying process has been shown to have minimal impact on the retention of these essential nutrients.
Micronutrients, such as iron, zinc, and calcium, as well as vitamins like vitamin A, vitamin E, and vitamin K, remain largely unaffected by freeze drying. This ensures that freeze dried milk continues to provide infants with the necessary micronutrients and vitamins for their overall well-being.
Studies Highlighting the Integrity of Freeze Dried Fat Content and Lipase
One important aspect of breast milk is its fat content, which plays a vital role in providing the necessary energy and supporting the development of infants. Research studies have shown that freeze drying preserves the fat content of breast milk better than traditional frozen breast milk methods.
The freeze drying process allows for the removal of water while maintaining the integrity of the fat molecules, resulting in a higher retention of fat content compared to frozen milk. Freeze drying also halts lipase enzyme from breaking down fats and stops the impact of lipase on the taste and aroma of the breast milk. These findings highlight the effectiveness of freeze drying in preserving the essential fat content of human milk.
Nutritional Testing and Supplementation Post Freeze Drying
After the freeze drying process, it is essential to ensure the nutritional integrity of the breast milk. Proper nutritional testing and supplementation play a crucial role in maintaining the quality and nutritional value of stored milk. Companies like BoobieJuice have conducted testing in-house and with 3rd party breast milk testing facilities to validate their processes and offer mothers the ability to pre and post test their very own breast milk and breast milk powder.
Professional Freeze Dried Human Milk
The scientific evidence supports the use of freeze drying as a method for preserving the nutritional properties of breast milk. By retaining the essential nutrients and immune factors that breast milk provides, freeze drying offers a convenient and reliable solution for parents and caregivers. The findings presented in this article should encourage individuals to consider freeze dried breast milk as a viable option for ensuring the well-being and nourishment of infants.
Learn more about the process and get started with BoobieJuice.
